Regulatory Segmentation
Segmentation algorithms partition the genome into regions with distinct epigenomic profiles. These are genomic regions of similar signal pattern over a selected number of assays.
To segment the genome for each cell type we currently use either ChromHMM (Ernst et al., 2011) or Segway (Hoffman et al., 2011). These algorithms detect recurring signal patterns, called states, from a collection of genome-wide assays, such as DNase-seq and ChIP-seq, across the different cell types. They then assign a state to each basepair per epigenome. Following this stage, the 25 states are assigned a functional label, including CTCF, Distal, Heterochromatin, Open Chromatin, Transcription Factor Binding Site, Gene, Predicted Weak enhancer/Cis-reg element, Proximal, Tss, Poised and Repressed, based on a decision tree.
ChromHMM uses a multivariate hidden Markov Model, training on the binary presence or absence of signal for each assay in 200 base pair bins over the whole genome. Segway runs a dynamic Bayesian network algorithm using real-valued signal data, trained over the ENCODE pilot regions (1% of the genome), and fitted over the whole genome.
For the currect release we use ChromHMM with 25 epigenomic states with 200 bp resolution. The human genome segmentation is based on ENCODE (ENCODE Project Consortium, 2012), Roadmap Epigenomics (Roadmap Epigenomics Consortium, 2015) and BLUEPRINT data. The assays were chosen to maximise information content about the state of the genome in each project. These assays (including control input sequencing) were coordinated across all cell types and constituted from three classes of data, which differ across projects due to data availability:
| Segmentation | Input Data Class | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Human ENCODE/Roadmap ChromHMM | Open chromatin | DNase1 hypersensitivity |
| Transcription factors | CTCF | |
| Histone modifications | H3K4me1, H3K4me2, H3K4me3, H3K9ac, H3K27ac, H3K27me3, H3K36me3, H4K20me1 | |
| Human BLUEPRINT ChromHMM | Histone modifications | H3K4me1, H3K4me3, H3K9me3, H3K27ac, H3K27me3, H3K36me3 |
Regulatory Segmentation in the Browser
There is one segmentation track available for each of the cell types in the Ensembl Regulatory Build. These tracks are off by default. To turn on the Segmentation tracks, you need to configure the page as shown below.
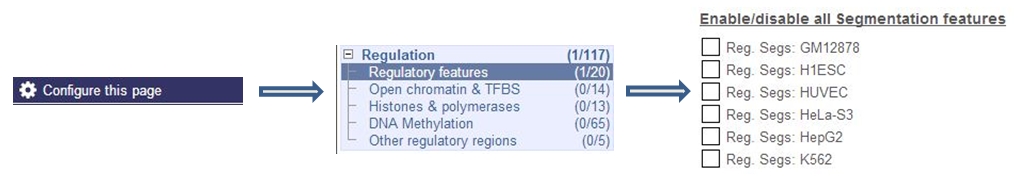
The colours used for each of the segmentation classes follows the the agreed ENCODE standard, explained in a legend displayed at the bottom of any window showing regulatory features.